What is Kaizen?
In today’s dynamic business environment, the key to staying competitive lies in continuous improvement. Kaizen, a Japanese philosophy meaning “change for the better,” provides the foundation for sustained operational excellence. It focuses on small, incremental changes rather than dramatic overhauls, making it an adaptable and powerful tool for long-term success.
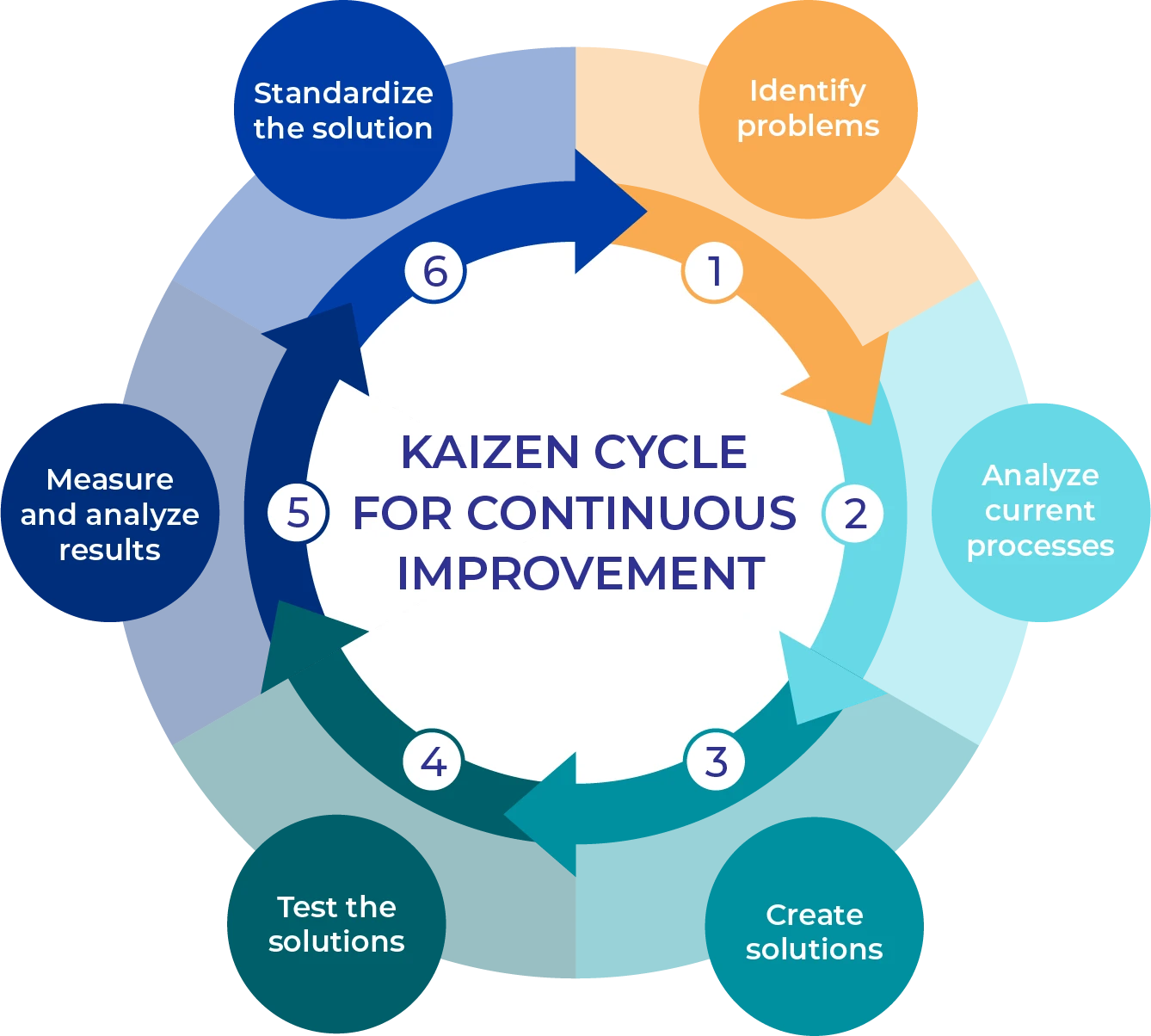
The Essence of Kaizen
Originally introduced by Masaaki Imai, Kaizen gained prominence during Japan’s post-war recovery and became integral to the Toyota Production System, a precursor to Lean Manufacturing. Today, Kaizen principles are widely applied across industries to improve efficiency, enhance quality, and reduce waste.
For a detailed introduction to Kaizen, refer to the Lean Enterprise Institute, which provides valuable insights into the philosophy and its applications.
Core Principles of Kaizen
Kaizen is built on five core principles that guide its implementation. Each principle encourages organizations to pursue continuous improvement in a structured and sustainable way:
1. Continuous Improvement
The essence of Kaizen lies in the belief that there is always room for improvement. Small, manageable changes build momentum over time, leading to significant cumulative benefits.
For real-life examples of continuous improvement, check out ASQ’s Quality Resources.
2. Employee Involvement
Kaizen emphasizes the importance of involving employees at all levels. Frontline workers, in particular, have valuable insights into daily operations and are instrumental in identifying inefficiencies.
3. Waste Elimination (Muda)
Kaizen’s focus on eliminating waste aligns closely with Lean Manufacturing principles. Waste, or Muda, can take many forms, including overproduction, waiting, excess inventory, and defects.
Learn more about the seven types of waste in Lean Manufacturing.
4. Standardization
Once an improved process is identified, it should be standardized and documented to ensure consistency. Standardization creates a baseline for future improvements while preventing teams from reverting to less efficient methods.
5. Proactive Quality Control
Instead of relying solely on end-stage quality checks, Kaizen builds quality into every step of the process. This reduces defects, minimizes rework, and ensures customer satisfaction.
For insights into proactive quality management, see ASQ’s guide to Total Quality Management.
How to Implement Kaizen: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing Kaizen involves a structured approach that fosters collaboration, accountability, and data-driven decision-making. Here’s how you can start:
1. Conduct Gemba Walks
The term “Gemba” means “the real place” in Japanese. A Gemba Walk involves observing processes directly where they happen, such as the shop floor, to identify inefficiencies.
Learn more about conducting effective Gemba Walks from 6Sigma.
2. Use the PDCA Cycle
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle ensures that changes are tested, evaluated, and refined before full implementation:
- Plan: Identify a problem and propose a solution.
- Do: Test the solution on a small scale.
- Check: Analyze the results to measure effectiveness.
- Act: Implement successful changes and standardize them.
3. Engage Cross-Functional Teams
Kaizen thrives on collaboration. Cross-functional teams bring diverse perspectives to problem-solving and help break down departmental silos.
4. Leverage Data and Analytics
Kaizen relies on measurable results. Use analytics tools to track KPIs like defect rates, cycle times, and equipment uptime.
Kaizen in Action: A Real-World Case Study
Case Study: Enhancing Manufacturing Operations with Kaizen
A manufacturing company faced challenges including high defect rates, frequent machine breakdowns, and low employee morale. Through a Kaizen initiative, the organization achieved transformative results.
- Identifying Problems: Gemba Walks and employee feedback revealed inconsistencies in maintenance procedures and a lack of training resources.
- Standardizing Solutions: The company digitized its maintenance workflows using VSight Workflow, ensuring that technicians had access to standardized procedures.
- Leveraging Technology: Real-time remote collaboration was introduced via VSight Remote. Experts guided technicians through complex repairs using augmented reality, significantly reducing downtime.
- Evaluating Results: Within six months, the company saw a 30% reduction in machine breakdowns and a 25% improvement in product quality.
The Role of Technology in Kaizen
1. Standardizing Processes with Digital Workflows
Tools like VSight Workflow help convert paper-based processes into interactive digital workflows, ensuring consistency and reducing human error.
2. Enhancing Collaboration with Remote Assistance
VSight Remote facilitates real-time collaboration between on-site workers and remote experts, enabling faster problem resolution.
3. Preserving Knowledge with Step-by-Step Videos
Using VSight VideoFlow, businesses can document expert knowledge in video format, creating a repository of best practices for training and guidance.
For insights into how AI intersects with Kaizen to drive continuous improvement, refer to Kazien.coms’s detailed article.
Conclusion: Achieving Excellence with Kaizen
Kaizen is more than a methodology—it’s a mindset that empowers organizations to achieve continuous improvement and sustainable growth. By integrating its principles with modern technologies like VSight Remote and VSight Workflow, businesses can amplify their results, streamline processes, and foster a culture of collaboration and innovation.
For more insights into Kaizen and its applications, explore the Kaizen Institute’s resources.
Are you ready to embark on your Kaizen journey? Contact VSight today to learn how our solutions can support your continuous improvement efforts.
Learn more about VSight
See how VSight can help you with your field service, maintenance, onboarding and training operations.